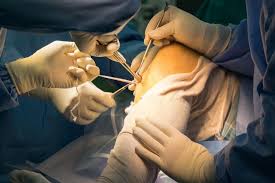
What is Arthroscopic Surgery?
Arthroscopic surgery, also known as arthroscopy, is a surgical technique used to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint. A small camera called an arthroscope is inserted into the joint through a tiny incision. The camera projects images onto a monitor, allowing the surgeon to guide miniature surgical instruments to repair damaged tissues.
Commonly treated joints include:
Knee
Shoulder
Elbow
Wrist
Hip
Ankle
What are the Common Conditions Treated with Arthroscopy?
Torn meniscus or ACL (knee)
Rotator cuff tears (shoulder)
Shoulder impingement or instability
Loose bone or cartilage fragments
Joint inflammation (synovitis)
Labral tears (hip or shoulder)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (wrist)
What are the Benefits of Arthroscopic Surgery?
Arthroscopic procedures offer several advantages over traditional open surgeries, including:
✅ Minimally Invasive
Arthroscopy uses small incisions, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues. This results in less pain and scarring.
✅ Faster Recovery
Patients usually experience quicker healing and can return to daily activities or work sooner than after open surgery.
✅ Lower Risk of Infection
Smaller wounds mean a reduced risk of post-operative infections and complications.
✅ Less Post-operative Pain
Because of the precision and minimal tissue damage, patients often require fewer pain medications.
✅ Outpatient Procedure
In many cases, arthroscopy is done on an outpatient basis, meaning no hospital stay is required.
✅ Accurate Diagnosis
Surgeons get a direct view of the joint, which helps in identifying problems more precisely than imaging tests alone.
What are the Risks and Complications?
While arthroscopy is generally safe, like all surgeries, it carries some risks:
⚠️ Infection
Though rare, any surgical procedure can lead to infection at the incision site or inside the joint.
⚠️ Blood Clots
In some cases, patients may develop clots in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), especially after lower limb surgeries.
⚠️ Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage
There is a small risk of injury to nerves or blood vessels during the procedure.
⚠️ Stiffness or Swelling
Some patients may experience joint stiffness or swelling during recovery, which can be managed with physical therapy.
⚠️ Incomplete Relief
Not all procedures guarantee complete pain relief. In some cases, additional treatment or surgery may be required.
What to Expect Before Surgery
Your orthopedic surgeon will:
Take your detailed medical history
Order imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or CT scans)
Explain the procedure, benefits, and risks
Discuss anesthesia options (usually general or regional)
You’ll also receive instructions on fasting and medications to avoid before the procedure.
What are the Recovery After Arthroscopic Surgery?
Recovery timelines vary based on the joint treated and the specific procedure performed.
🔹 Immediately After Surgery
The area will be bandaged and possibly immobilized with a brace or sling.
You may feel groggy from anesthesia for a few hours.
Pain and swelling are managed with medications and cold therapy.
🔹 First Few Days
Rest and elevate the joint to minimize swelling.
Start gentle movements as recommended.
Crutches or slings may be needed temporarily.
🔹 1 to 3 Weeks
Sutures are usually removed within 7–10 days.
You may begin physical therapy.
Gradual improvement in joint function and range of motion.
🔹 4 to 8 Weeks
Increased strength and mobility with consistent rehab.
Return to light work and daily activities.
🔹 2 to 3 Months
Full recovery for minor procedures.
Athletes and active individuals may need additional time and rehab to return to sports.
Post-Surgery Tips for a Smooth Recovery
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Attend all physiotherapy sessions.
Avoid strenuous activities or lifting until cleared by your doctor.
Eat a balanced diet to support healing.
Watch for signs of infection (redness, fever, excessive swelling).